Quest to Discover the Nature of 70 Percent of the Universe
How would you feel if you purchased a house and you knew the total square footage of the home, but were locked out from access to 70 percent of the house? Wouldn’t you be curious about the nature of that 70 percent? Wouldn’t you attempt to enlist the assistance of a locksmith to gain access to that 70 percent?
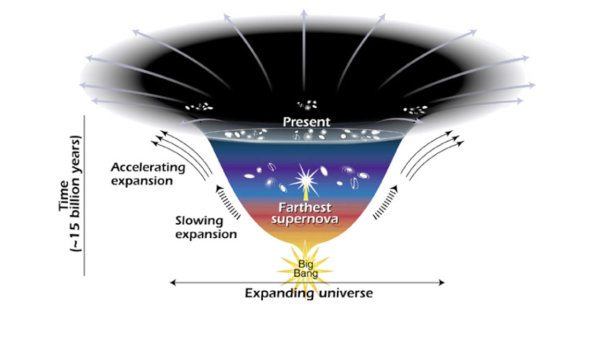
How you would feel and respond to being locked out of 70 percent of a house describes well the drive and curiosity astronomers express about the nature of dark energy. As I described in my blog post on April 23, astronomers’ recent analysis of measurements on 1,133,326 galaxies from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey showed that dark energy makes up 69.9 percent of all the stuff of the universe.1 What astronomers know so far about the stuff that comprises 69.9 percent of the universe is that it is an unknown form of energy that permeates the universe’s entire space surface so as to tend to accelerate the universe’s expansion rate. However, even though astronomers are now convinced that dark energy is the dominant component of the universe and that it is the factor either entirely or mostly responsible for the accelerating expansion of the universe, they still know little about its fundamental properties and nature. Hence, a massive search is underway to discover the specific nature of dark energy.
In my April 23rd blog post, I reported on how an analysis of the sample of 1,133,326 galaxies indicated that the acceleration of the cosmic expansion rate was consistent with dark energy being governed by a single nonvarying constant, otherwise known as the cosmological constant. Specifically, the analysis determined that w = -1.042 ± 0.067, where w = P/ρ, where P and ρ denote dark energy’s pressure and energy density respectively, and w exactly = -1.0, which means that dark energy is governed by a single nonvarying constant.
In a paper published in the April 10 issue of the Astrophysical Journal, a team of ten astronomers (including one I knew personally from my time at Caltech), based on measurements of 1,364 supernovae, determined that w = -0.989 ± 0.057.2 Both this determination and the one I reported on in my April 23 blog post were predominantly based on cosmic expansion rate measures of galaxies closer to us than 10 billion light-years. That is, they were determining the properties of dark energy for the last 9 billion years of cosmic history, but not so much for the first 5 billion years of cosmic history.
In the same issue of the Astrophysical Journal, three Chinese astronomers—Ji-Ping Dai, Yang Yang, and Jun-Qing Xia—reconstructed w from the latest observations that included type Ia supernovae, the cosmic microwave background radiation (radiation left over from the cosmic creation event), the universe’s large-scale structure (go here for a mind-blowing video clip of the development of the cosmic large-scale structure), measurements of the cosmic expansion rates based on objects nearer than 9 billion light-years, and baryon acoustic oscillations.3 They found that this reconstruction was consistent with w = -1.0. However, when they added in the baryon acoustic oscillation determinations based on measurements of the Lyman α forest of spectral lines seen in quasars at distances ranging from 9 to 13.5 billion light-years, they noted “a strong preference for the time-evolving behavior of dark energy.”4
In other words, Dai, Yang, and Xia’s study indicates that while dark energy appears to show no evolution over the past 9 billion years, dark energy may indeed be evolving over the first 4.8 billion years of cosmic history. They close their paper with an appeal for astronomers to use the next generation of telescopes to gain more accurate and comprehensive observations of the Lyman α forest of spectral lines in distant quasars to determine the true nature of dark energy.
A team of five astronomers in France, Germany, and the United Kingdom used an entirely different method to constrain w. They used measurements of the thermal Sunyaev Zel’dovich power spectrum to establish that w = -1.10 ± 0.12.5 Three other astronomers explained how the Square Kilometre Array radio telescope (construction to begin in 2019), through measurements of the 21-cm spectral line of neutral hydrogen in very distant quasars and galaxies, will definitely provide an accurate measure of the nature of dark energy during the first few billion years of cosmic history.6

Figure: Artist’s Impression of the South African Half of the Square Kilometer Array. Image credit: SKA Project Development Office and Swinburne Astronomy Productions
In the last few months, astronomers have made significant progress in determining the nature of dark energy. The new generation of optical telescopes (e.g., the Extremely Large Telescope), infrared telescopes (e.g., the James Webb Space Telescope), and radio telescopes (e.g., the Square Kilometre Array) promises to accurately nail down the properties of dark energy. When that happens, we will know what is going with 70 percent of the universe. That knowledge undoubtedly will unveil yet even more evidence for the fine-tuning design of the universe that makes the existence of physical life, and human life in particular, possible.
Endnotes
- Hugh Ross, “Million Galaxy Study Yields Improved Cosmic Creation Model,” Today’s New Reason to Believe (blog), Reasons to Believe, April 23, 2018, http://www.reasons.org/explore/blogs/todays-new-reason-to-believe/read/todays-new-reason-to-believe/2018/04/23/million-galaxy-study-yields-improved-cosmic-creation-model.
- D. O. Jones et al., “Measuring Dark Energy Properties with Photometrically Classified Pan-STARRS Supernovae. II. Cosmological Parameters,” Astrophysical Journal 857 (April 10, 2018): id. 51, doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aab6b1.
- Ji-Ping Dai, Yang Yang, and Jun-Qing Xia, “Reconstruction of the Dark Energy Equation of State from the Latest Observations,” Astrophysical Journal 857 (April 10, 2018): id. 9, doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aab49a.
- Dai, Yang, and Xia, “Reconstruction of the Dark Energy Equation,” page 1 of id. 9.
- Boris Bolliet et al., “Dark Energy Constraints from the Thermal Sunyaev Zeldovich Power Spectrum,” Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. Published ahead of print, March 29, 2018. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty823.
- Bikash R. Dinda, Anjan A. Sen, and Tirthankar Roy Choudhury, “Dark Energy Constraints from the 21-cm Intensity Mapping Surveys with SKA1,” eprint arXiv:1804.11137 (April 2018), https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.11137.
Check out more from Dr. Hugh Ross @Reasons.org